未来,也许只需运送一台3D打印机到太空,航天员就可以在太空自主打印所需的物品。为了早日实现“太空制造”梦想,中国航天科技集团公司上海航天技术研究院积极发展3D打印技术,目前已成功联合研制出首台航天多激光金属3D打印机。
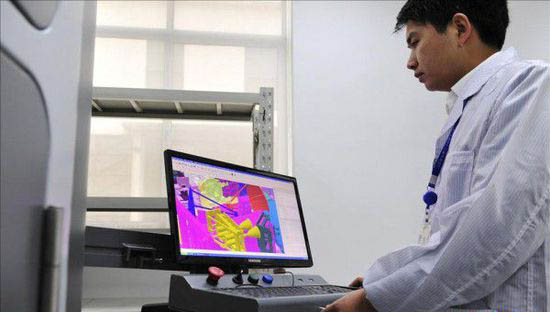
记者在上海航天技术研究院看到,这台3D打印机看上去形如一个银灰色柜子,柜子左上侧设置了一个小小的玻璃窗,右上侧设置了电脑及键盘,制作人员在电脑上输入需要打印的模型,放入粉末状的打印材料,按下打印键,就可以从玻璃窗里看到,打印材料被一层层地送入到打印区域,从底部向上打印,机器不断循环“送粉-铺粉-激光熔化”过程,粉末每铺一层,激光束便会选择熔化相应的零件截面图形,然后以每层0.02毫米的厚度逐层添加粉末,最终完成金属激光熔化的生产过程。
据上海航天技术研究院高级工程师王联凤介绍,这台3D打印机采用双激光器,一种是长波的光纤激光器,另一种是短波的二氧化碳激光器,可以打印长宽高不超过250毫米的物品,每小时可打印8立方厘米,打印材料为不锈钢、钛合金、镍基高温合金等。这种双激光金属选区熔化3D打印机的相关技术,目前已申请多项国家专利。
根据应用需求,首台航天3D打印机已成功打印出卫星星载设备的光学镜片支架、核电检测设备的精密复杂零件、飞机研制过程中用到的叶轮、汽车发动机中的异形齿轮等构件。这些构件有的为网状镂空结构、有的形状极其不规则、有的微小而复杂,如果采取传统加工技术,不仅造价昂贵、废品率高,甚至难以加工生产。而这台航天3D打印机很快就能打印出来。经过测试,这些打印的零件性能满足工程化应用要求。
“航天产品型号众多、结构复杂,要求多品种、小批量、轻量化生产,3D打印技术有广阔的应用前景。但与此同时,航天也对质量要求极其严格,我们打印出来的产品还需进行严格测试后,才能最终应用于航天。”王联凤说。
来源: 新华网上海12月7日电(记者张建松)
Scientists in China have developed a new Additive Manufacturing (AM) machine, the first of its kind in China, that will allow astronauts to produce a range of items made from stainless steel, titanium alloy and nickel-based superalloy, whilst in space.
According to Wang Lianfeng, a Senior Engineer with the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASTC) in Shanghai, the machine is capable of printing products such as optical lens brackets used in space borne equipment, complicated components used in nuclear power testing equipment and impellers used in aircraft research.
“The products made will have to be tested thoroughly, due to the strict quality requirements of aerospace products,” stated Wang, adding that the prospect for 3D printing is promising.
The dual laser AM machine uses both long-wave fibre and short-wave carbon dioxide lasers and has a build size of up to 250 mm. Several patents have been applied for.
(From www.metal-am.com)